The principle of parsing collimated light exposure machine and graphic transfer technology
With the demand for high-precision imaging of electronic products, the requirements for the design and manufacture of printed circuit boards are also increasing. This has led to the development of exposure equipment needed for PCB production. The development of parallel light exposure equipment for this purpose is the key to making dense, thin lines. The article introduces the working principle of the parallel exposure machine and the graphic transfer technology. Follow the small series to learn more about it.
Parallel light exposure machine featuresThis type of device has only one lamp, and the exposure table is also divided into two mirrors above and below, using the principle of light refraction. When two surfaces are exposed at the same time, the exposure of the upper and lower lights is separated. The first exposure is performed first, and a mirror reflects the light to the upper mirror of the table and then refracts to the exposure table. When the lamp is exposed, the light is directed directly into the mirror below and then refracted onto the table. Therefore, when the exposure machine is used for exposure, the energy of the lamp will be greater than the energy of the lamp. Exposure and level The number will be the same.
Parallel light exposure machine working principle1, light source
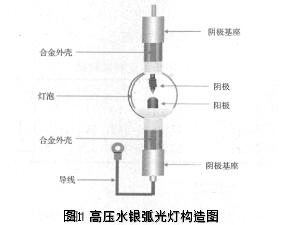
Figure 1 is a high pressure mercury arc lamp configuration diagram. The light source required for dry film exposure in the printed circuit board process is mainly near-ultraviolet light with a wavelength range of 400 nm to 300 nm. The ultraviolet light source is mainly a mercury arc lamp. When the current passes through a glass filled with inert gas and metal vapor, the arc is generated. The simple principle is that the free electrons in the sealed tube have sufficient energy after being accelerated by the electric field, and the ionized reaction can be caused by the inert gas (for example, helium) that is collided with it. After the collision, the positively charged antimony ions go in the direction of the opposite electrode, and when they encounter electrons, they combine with each other and become neutral. Because of its collisions and the positive and negative bound energy, an excited helium atom is produced. The excited deuterium atoms have a longer life and can be transferred to the simultaneous presence of metal vapors (eg, mercury atoms) in the sealed tube, causing them to also be excited. This excited mercury releases energy by releasing light energy to return to a stable state. This is how the arc lamp shines. The following reaction formula:
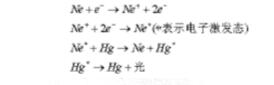
2, light path
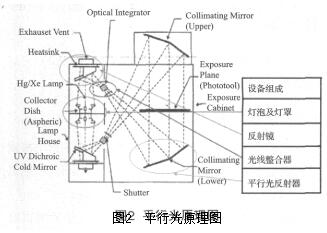
Figure 2 is a schematic diagram of the principle of parallel light, the light emitted by the light source, part of the light through the condenser, and then through the medium of the cold mirror or two-way aluminum mirror, and reflected out; these two kinds of mirror can also be used as infrared filter The bi-directional aluminum mirror allows the infrared light in the light source to pass through, and the heat is absorbed by the heat sink. The remaining cold light is refracted at 90° through a combination of other lenticular lenses (generally called Light Integrator). At this time, the infrared light is filtered away, leaving almost all of the pure UV light, which is an appearance. The blue light has a wavelength between 320 nm and 405 nm. Then it reaches two other reflective surfaces, generally called collimated light reflectors, which become parallel light rays that reflect off and reach the work area.
1, dry film
The photosensitive material medium consists of three layers: a polyester film base, a photosensitive resist film, and a polyethylene protective film. The film base is a carrier of a photosensitive resist film, so that the resist dry film maintains good dimensional stability, and the resist film can also be protected from wear; the photosensitive resist film is composed of a photosensitive resist resin; The acrylic or polyethylene film is a protective layer covering the other side of the resist layer.
2, film
The film is a graphic transfer medium, as shown in Figure 3.

3, the principle of graphics transfer technology
The photochemical reaction of ultraviolet light through the pattern transfer medium (black sheet) and the photosensitive material (dry film) causes changes in the chemical structure within the polymer or between the macromolecules, resulting in changes in the physical properties of the photosensitive polymer, and its chemistry Poor activity. The unirradiated chemical reaction does not occur, the activity does not change, and the reaction part has a low chemical activity. Using this characteristic, a conductive pattern is formed by dissolving or stripping.
4, dry film graphics transfer process
The parallel light exposure machine is mainly used for photoresist exposure.
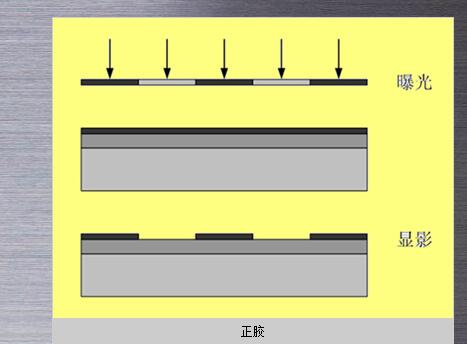
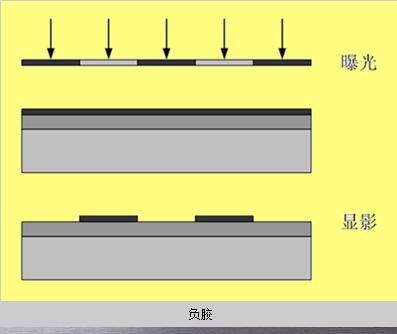
Photoresist, also known as photoresist, is a photosensitive material that changes its properties when exposed to light. The photoresist is mainly used to transfer the pattern on the lithography mask onto the wafer.
Photoresist is divided into positive and negative glues. After the positive adhesive is exposed, the light-irradiated portion becomes easily dissolved, and is dissolved after the development, leaving only the unilluminated portion to form a pattern. However, negative adhesive is just the opposite. After exposure, the exposed portion becomes difficult to be exposed. Dissolve, after the development, leaving the light part to form a picture.
Negative photoresist was first used in the photolithography process, and its process cost was low and the yield was high. However, because it absorbs the developer solution and swells, its resolution (ie, the minimum pattern that can be opened in the photolithography process) is not as good as that of the positive resist. For submicron and even smaller processing technologies, positive photoresist is mainly used as a photoresist.
Heating Pad For Feet,Heating Pad For Foot,Foot Heating Pad,Cordless Foot Warmer
Ningbo Sinco Industrial & Trading Co., Ltd. , https://www.newsinco.com