Standards development will start the 5G concept and technology route gradually clear
With the vigorous promotion of the global industry, the fifth-generation mobile communication (5G) technology has developed rapidly and has now entered a critical stage where concept formation and standard setting work are about to start. In order to promote the formation of the global 5G concept, China's IMT-2020 (5G) promotion team conducted in-depth research on 5G main scenarios, technical requirements and key technologies, and refined the 5G concept and technical route. In terms of standardization, the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) is about to complete the preliminary research of the 5G standard, and clearly proposes the IMT-2020 standard work plan. The 3GPP, the international mainstream mobile communication standards organization, has also recently launched a discussion on 5G related topics.

5G faces four major technical challenges
For 2020 and beyond, mobile Internet and Internet of Things will become the main driving force for 5G development. 5G will meet the diverse business needs of people in various scenarios such as living, working, leisure and transportation. From the requirements of the mobile Internet and the Internet of Things, the four main technical scenarios of 5G can be extracted: continuous wide-area coverage scenarios, hot-spot high-capacity scenarios, low-power large-connection scenarios, and low-latency and high-reliability scenarios. The first two scenarios are mainly for mobile Internet applications, and the latter two scenarios are mainly for IoT and vertical industry applications.
5G faces multiple technical challenges in four major scenarios. The continuous wide-area coverage scenario adopts the most basic coverage mode of mobile communication, and needs to provide users with a user experience rate of more than 100 Mbps anytime and anywhere; the hot-spot high-capacity scenario faces the local hotspot area, and needs to meet the extremely high data transmission rate of the user and the inner range of the region. High data traffic requirements, main challenges include 1Gbps user experience rate, tens of Gbps peak rate and tens of Tbps/km2 traffic density; low-power large connection scenarios are mainly for massive low-power IoT applications, requiring not only 5G networks With a total connection capacity of over 100 billion devices and a connection density requirement of 1 million square kilometers, it is also necessary to ensure ultra-low power consumption and ultra-low cost of the terminal; low-latency and high-reliability scenarios are mainly oriented to verticals such as vehicle networking and industrial control. The demanding requirements of the industry require millisecond end-to-end delay and near 100% reliability.
5G innovation comes from both wireless and network
Different from previous generations of mobile communication technologies, the source of 5G technology innovation will be more abundant. Not only will wireless technologies undergo major innovations, but also network technologies will undergo major changes.
In terms of wireless technology, 5G will adopt four core technologies: large-scale antenna array, ultra-dense networking, new multi-access and full spectrum access. Large-scale antenna arrays can support dozens of independent spatial data streams by increasing the number of antennas, which can increase system spectral efficiency and capacity several times. Ultra-dense networking can greatly increase the efficiency of frequency reuse by increasing the density of base stations. The new type of multiple access transmits the signal in the code domain/space/time/frequency domain, which can significantly improve the spectrum efficiency and access capability of the system in multiple scenarios, and can reduce the signaling overhead and time through the unscheduled transmission. Extending the power consumption of the terminal, potential technical solutions include SCMA, MUSA, PDMA and NOMA. Full spectrum access can effectively utilize various mobile communication spectrum to increase the transmission rate. Among them, the frequency band below 6 GHz is better, and can be used as the 5G preferred frequency band; the frequency band above 6 GHz can be used as the subsequent supplementary frequency band. In addition, FBMC, F-OFDM, full-duplex, flexible duplex, D2D, multi-LDPC code, network coding, polarization code, etc. are also considered as potential 5G wireless key technologies.
In the face of diverse 5G scenarios, appropriate wireless technologies are needed to meet the needs.
——In continuous wide-area coverage scenarios, large-scale antenna arrays can greatly improve system spectrum efficiency and improve user experience rate. It is one of the most important enabling technologies for continuous wide-area coverage scenarios. New multi-access technology can be used with large-scale antenna arrays. Together, it further enhances spectrum efficiency and multi-user access.
——In hot-spot high-capacity scenarios, ultra-dense networking can greatly improve the frequency reuse efficiency per unit area, and can be combined with large-scale antenna arrays and new multi-access to further improve system spectrum efficiency, and full spectrum access can Take advantage of low frequency and high frequency resources to achieve higher transfer rates and greater system capacity.
——In the low-power and large-connection scenario, the new multi-access can double the system's device connection capability, and can reduce the signaling overhead and terminal power consumption through the non-scheduled mechanism; F-OFDM and FBMC can flexibly use the fragment spectrum to support Narrowband and small data packets, and reduce power consumption and cost; D2D can avoid long-distance transmission between base stations and terminals, thereby reducing power consumption and improving transmission efficiency.
——In low-latency and high-reliability scenarios, short-frame structure and streamlined signaling procedures should be adopted, and new technologies such as multiple access and D2D should be introduced to reduce signaling interaction and data transfer, and more advanced modulation coding and weighting can be adopted. Transmission mechanism to improve the reliability of transmission.
In terms of network technology, 5G will adopt the new network architecture of “three cloudsâ€, and the whole network will be more flexible, intelligent, efficient and open. The 5G network will use SDN and NFV as the basic enabling technologies. The network architecture can be divided into three domains: access cloud, control cloud and forwarding cloud. The access cloud supports multi-standard wireless access, and integrates centralized, distributed and Mesh radio access network architectures to adapt to various types of backhaul links, enabling more flexible networking deployment and more efficient radio resource management. The 5G network control function and data forwarding function will be decoupled to form a centralized and unified control cloud and a flexible and efficient forwarding cloud. Control the cloud to achieve local and global session control, mobility management and service quality assurance, and build a business-oriented network capability open interface to meet the differentiated needs of the business and improve the efficiency of business deployment. The forwarding cloud is based on a general-purpose hardware platform, and under the high-efficiency control of the control cloud, it realizes high-reliability, low-latency, and efficient transmission of massive business data.
5G concept and technical route
With integrated needs and technology trends, the 5G concept can be defined by a combination of “signature capability indicators†and “a set of key technologiesâ€. The user experience rate is recognized by the industry as the most important performance indicator of 5G. It reflects the real data rate available to users and is the most closely watched performance indicator. According to the technical requirements of the 5G main scenario, the 5G iconic capability indicator should be “Gbps user experience rateâ€. In terms of key technologies, 5G will adopt a set of key technologies including large-scale antenna array, ultra-dense networking, new multiple access, full spectrum access and new network architecture to meet the different needs of various scenarios.
From the perspective of mobile communication technology, standards and industry development trends, 5G has two technical routes: new air interface and 4G evolution. The new air route is mainly designed for new scenarios and new frequency bands. It does not consider compatibility with 4G frameworks. It can meet the business needs and challenges that cannot be met by the 4G evolution route through new solution design or introduction of innovative technologies. IoT scenarios and high-band application requirements. By introducing enhanced new technologies on the existing 4G framework, the 4G evolution route can further improve system performance while ensuring compatibility, and can meet 5G scenarios and service requirements to a certain extent. In addition, the next-generation wireless LAN (IEEE 802.11ax) will become an important complement to 5G and will be integrated with 5G to provide services to users.
Since 2012, the ITU has organized the global industry to carry out preliminary research on 5G vision and technology trends to reach a global consensus on 5G. With the above work gradually coming to an end, the ITU recently released the IMT-2020 work plan, which will start the 5G technical performance requirements and evaluation method research in early 2016, start the 5G candidate proposal collection at the end of 2017, and complete the standard formulation by the end of 2020.
As the international mainstream mobile communication standards organization, 3GPP recently launched a discussion on 5G issues. In February 2015, the SA1 Working Group launched a research on future new business needs; in March 2015, the RAN Working Group also launched a 5G discussion, and plans to hold a 5G seminar in September 2015 and launch a 5G access network by the end of 2015. Pre-research work such as demand and channel model. It is expected that the official 5G standard research project (SI) will be launched in 3GPPR14, and the 5G standard work project (WI) will be launched in the R15 phase, and the 5G standard will be further refined in R16 and later.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is the network of physical devices, vehicles, batteries, home Appliances, and other items embedded with electronics, software, sensors, actuators, and connectivity which enables these things to connect and exchange data, creating opportunities for more direct integration of the physical world into computer-based systems, resulting in efficiency improvements, economic benefits, and reduced human exertions.
Our Battery Remote Monitor with IoT is direct integration of the battery restore solution and device into computer-based battery monitoring system which combines wireless communication with patented, field-proven battery monitor and analysis technology. It not only has the ability to restore battery, but also has the ability to monitor battery's State-Of-Health(SOH) in real time.
Uptime is the most basic requirements in nowadays connected to all things in the world. Power systems rely on batteries to provide critical backup energy and power in sudden affairs. When power supply of normal grid is lost suddenly, the backup power systems must perform. Without proper monitoring of the back up power system status whether safe or not, there is a irreparable risk of catastrophic loss for Hospital institution, Telecommunication cost, financial organizations and even the army suddenly lost the war, etc.
How our Battery Remote Monitor IOT works? it is comprised of 3 base hardware devices and 1 software operation system. The monitor parts connected with batteries pack and reliably reports battery State-Of-Health(SOH) to the software platform. Wirelessly enables these monitoring hardware to connect and exchange data with users in working to control the batteries status in real time.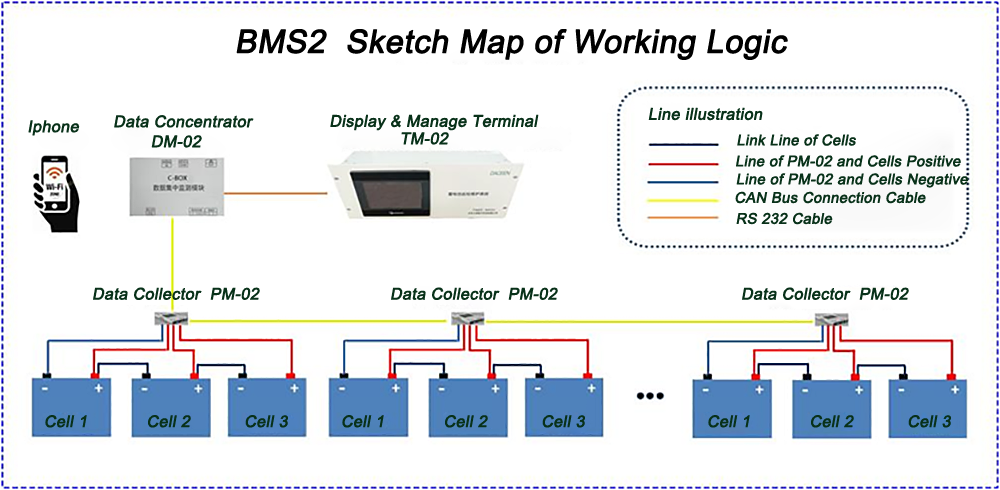
Our family members of Battery Remote Monitor IoT are Battery Smart Pulse Protector with BlueTooth and GPS tracking management such as Car or Truck GPS System , Telecom Base Site Battery Protector System with wireless monitor, Battery Smart Remote Monitoring system and Battery Anti-Theft GPS System, etc.
Battery Remote Monitor IOT
Battery Remote Monitor IOT,Battery Remote Monitor IOT,Battery Remote Monitoring,Home Battery Remote Monitoring,Monnit Temperature Sensor
Shenzhen Daceen Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.daceen-sz.com