The Theory and Practice of the Appraisal of Archives Value (5) —— Thinking about the Appraisal of Electronic Documents
The identification of Liu Yuenan from the School of Archives of Renmin University of China is the most difficult and most controversial part of the archival work. The emergence of electronic files has increased the complexity and difficulty of this work. In the 21st century with the rapid development of computer technology and communication technology, electronic documents will increasingly become the subject of the material objects of documents and archives. The results of the appraisal work are related to the ability to select materials that reflect all aspects of contemporary society for future generations. Therefore, the identification of electronic documents It is an important practical issue; at the same time, in the process of archivists changing from "passively keeping history", electronic document identification is the key factor and fuse that triggers the transformation of archive management theory. This work involves many important The issue of management thinking, the final determination of the electronic document identification method will reflect the new concept of people managing and using document information in the information age. If the electronic document identification method is regarded as a system, then the following question must be answered during the design of the method system: for whom is the identification of the electronic file conducted for whom? This simple question contains deeper connotations , Related to the establishment of the value subject of electronic documents, and directly affect the choice of identification methods. The question of who is appraising archives has historically yielded several answers: rulers, document creators, academic researchers (mainly historical researchers), and citizens of the whole society. It can be said that every progress in understanding is inseparable from the improvement of the social, political and cultural environment at that time, and is consistent with the democratization process and the strengthening of communication. Since "archives are the arsenal of the ruling class"
And ruthlessly destroy archives that are not conducive to rule; to "archives are the think tanks of historical research," use historians' opinions as the main standard to measure the value of archives; then, "archivists should not be tightly tied to academics Under the fashion of the market ", it should reflect" the vast territory of human life. "Otherwise," the archivist at best is only a "vane" that changes with the history of the chronicle. That is, it should be the archives of all citizens. History clearly reflects the guiding principles of archives identification The evolution process reflects the process of continuous adjustment and positioning of the archive value subject.
The subject of file value is the user of the file, and the file identification is essentially a selective work for the user. In the era when citizens ’right to use archives had not been established, the ruler was the user of the archives, so the appraisal work was based on the interests of the ruling class, resulting in many archives not being preserved intact. Before the institution transfers the archives to the National Archives, the institution does not provide the society with the duty to use the archives, so it is generally in the interest of the unit to retain or destroy the archives spontaneously. Since the end of the 18th century, the use of archives has been a citizen ’s right that has been written into the relevant codes by various countries. However, because most citizens have not started to use this right consciously, for a long period of time, researchers have become Synonymous with user. With the progress of society, the demand for ordinary citizens to use documents and archives information is becoming stronger and stronger, such as requiring transparency of government offices, disclosure of business performance, and research on family history. The emergence of electronic computer technology and network technology has provided powerful tools for ordinary citizens to use archive information. Especially with the popularity of the Internet, the Internet has promoted the actual use of documents due to its unique openness, equality and easy accessibility. The user group of archive information has grown exponentially, and the most rapidly growing user type is non-expert users. ③ Therefore, if in a paper environment, "the use of archives is a citizen's right" is still a piece of paper to a greater extent, computer technology is the medium that enables it to be truly implemented. In the era of electronic documents, archives use The scope of the people is throughout the whole society, and the use needs and interests are more diversified. The archives department will use the new technology platform to provide "social memory" for social services. As a result, the file management model has gradually changed from the "national model" to the "social model". Therefore, as a whole, the identification of electronic files is carried out for all users and all citizens, and the identification of electronic files for all users is all The sum of the tasks of the archives department. Specific to a certain archives department, especially the internal archives department, the scope of existing users is often smaller than that of all citizens. When determining the standards for the identification of electronic documents, it is necessary to respect the needs of internal users of the organization and also consider the external users of the organization. need. Otherwise, it is easy for all users to verify that the electronic files are easy to fall into empty slogans.
Who can appraise who can represent and select all electronic files for the interests of all users to select and evaluate electronic files fairly? The question of "whoever spends the file appraisal work" has historically had two of the most representative and opposing views: , Represented by Hilary Jenkinson, believes that the person who formed the document is a suitable candidate for archival appraisal, and second, with Schellenberg as the representative, thinks that archivists can be qualified for appraisal work. Because the document appraiser appraise the document, because it only represents the interests of the department, it is easy to ignore the "second value" of the document, and the archivist appraisal of the document is easy to destroy the connection between the documents due to unfamiliar business.
In view of this, China has adopted a three-in-one approach of archival staff, business personnel and relevant leaders. By reading about the road of cooperation in recent years at home and abroad. The theoretical basis of the macro appraisal strategy is the “source-based structural function†appraisal method, which transfers the appraisal center from the document to the society and government that form the document and give the document meaning to the extensive connection with the “post custody modelâ€. The gist is consistent. The specific implementation steps of the macro appraisal strategy are: According to the importance of the status and functions of the various agencies of the Canadian federal government, more than 100 government document generation agencies are classified, and the National Archives have signed agreements with them in order to clarify each in the process of mutual cooperation For the obligations undertaken, the two parties shall negotiate to formulate the file retention schedule and work plan of each filing unit. The specific appraisal work shall be carried out by government agencies, and the archives shall provide services and guidance, and shall be managed according to law. ⑤ "Macro identification strategy" representing a model of the application of new theories in the era of electronic documents
The question of "who is identified" coincides unexpectedly with our country's long-term approach. However, there are also differences between the two. The members of the appraisal team in the "Macro Appraisal Strategy" are staff from national archives, leaders of government agencies, business personnel, and file and archive staff. It is to formulate a document storage period table. After the storage period table is completed, it can be operated by the archives staff of the institution. The National Archives will guide and manage the operation process. The organization form of the “three aspects combination†in China is generally an inter-departmental cooperation within an existing institution. The focus of cooperation is to determine the value of specific archives. The retention period table and relevant professional archives retention period table can be used as the basis, and does not need to obtain the approval of the superior archives administrative department, so there is rarely a phenomenon of cross-institution cooperation.
No matter what kind of carrier's document, the appraisal members are no different in judging the value of the document content. The electronic file has the characteristics of perishability, changeability, hardware and software environment dependence, etc., prompting the archives to reconsider the suitable person for the identification work. In 1984, Harold. Naugler wrote a "Document and Archive Management Planning (RAMP) survey report on the identification of machine-readable documents, pointing out that in addition to analyzing the content of electronic documents (also called content identification), the document recording method and Based on the nature of the carrier, the technical identification of electronic files is carried out. â‘¥ The dual identification of electronic files has been agreed in the field of archival theory and real. Since most archivists and business personnel are not familiar with emerging information technology, they undertake technical identification work There is a certain degree of difficulty, which leads to the introduction of technical personnel into the electronic file identification team. For example, the National Archives has handed over the electronic file identification work to the electronic file center. The reason is that the center has more than other places. Many professional and technical personnel.
By comparing the similarities and differences in the composition of Chinese and foreign file appraisers, and combining the characteristics of electronic files, we can explore the organization of electronic file appraisal suitable for China's national conditions. First of all, based on the identification of electronic documents should be based on both the macro and micro levels, taking into account the first value and the second value of the document, the dual identification of technology and content, so the combination of identification by multiple parties is essential. Secondly, because there are many types of institutions that carry out archival work in China, different types of institutions can adopt different combinations according to their needs. For example, for government agencies, in addition to inter-departmental cooperation within the unit, it is best to have (or be instructed by) personnel from the archives administration department or comprehensive archives when formulating the file retention schedule. As far as state-owned enterprises are concerned, unless they voluntarily voluntarily, they generally do not need the direct intervention of the personnel of the archives administrative department or the comprehensive archives. If the archivist's computer technology level is relatively high, the participation of technical personnel may not be required; if the technical personnel are indeed required to participate, he or they do not necessarily have to participate in the entire process of the identification work.
How to appraise the content appraisal method and the functional appraisal method are the two basic methods used in the identification of electronic documents: the key of the former is to judge the value of the electronic document by reviewing its content, represented by the National Archives of the United States; the latter is used to judge the formation of electronic documents The functional activities are centered on Canada, the Netherlands, Australia, Germany, etc. In comparison, the functional appraisal method has received a relatively high response in China's archive theory community. Hans Boms ’explanation is very persuasive. He believes that judging the value of documents by indirectly understanding the functions of those important document-formers who fulfill social needs and aspirations can reflect“ social dynamics and public opinion †, Thereby increasing the objectivity of identification and reducing arbitrariness. ⑧ This view has such a wide range of influence, in the final analysis, because it is consistent with the goal of "identifying archives for all users (ie, the public)": the operation of society is achieved through the performance of the functions of various institutions Yes, documents are the true records of functional activities. The value of documents depends on the importance of functional activities. Therefore, the identification of documents based on functional factors can more objectively reflect the true state of society in various historical periods. This method is based on document generation Reason, rather than the interests or interests of a certain part of the user, thus overcoming the subjectivity in the identification process and avoiding "causing the needs of those groups with the most lobbying voices or the disciplines where archivists are most willing to cooperate" "The storage of documents lags behind the new requirements of the researchers", and the realization of "use follows rather than leads the appraisal", ⑨ ultimately makes the appraisal results meet the needs of all people instead of some users.
But is the content appraisal method and the function appraisal method really incompatible? Can the real experience of the National Archives over the years be easily denied? In fact, as early as half a century ago, the appraisal of American documents included "each "The functional characteristics of the office" and "is this function an auxiliary function or a basic function"; other file theorists in the United States have also discussed the problem of function identification, such as the identification of archives and manuscripts by Maynard Bridgeford in 1977 The functional factors are also discussed in "Receiving and Receiving"; in 1993, "Selection and Appraisal of Archives and Manuscripts" by Geraldham also mentioned functions and functional appraisals. 1 This shows that the "content appraisal method" is not Eliminate functional factors, but evaluate the value of documents on the basis of institutional functions. Most importantly, the "content identification method" is not an identification method used purely to satisfy the interests or interests of some users.
At the same time, functions are not the only important criteria for electronic document identification.
If only the "identification work is focused on the functions or working procedures that form the document, rather than the document itself" "abstractly judge whether the document formed by a functional activity needs to be saved" without reading the document content, this method is in operation There will be unavoidable loopholes in the process. For example, a functional activity of the United States Patent and Trademark Office (PTO) is to approve patent applications. In 1996, the National Archives and Documents Administration evaluated the patent documents in 54 electronic systems of the Office. If only functional factors were considered, It was concluded that all 54 databases should be kept permanently. In fact, after examining the actual contents of the database, the archivist finally determined that only one database had permanent preservation value. Terry Cook, an active advocate of the “Functional Appraisal Method†later stated that archivists must consult the content of documents during appraisal. 1 Therefore, the functional appraisal method and the content appraisal method are not diametrically opposed. It is the foundation, and the content appraisal method is complementary. The functional appraisal method focuses on clarifying the boundary between documents with and without preservation value, and the documents formed in important functional activities and representative secondary functional activities generally have preservation value, and large The documents formed in most secondary functional activities either have no preservation value or have less preservation value; while the content identification method focuses on further depreciation of documents with preservation value, different documents formed in the same functional activity may It has different preservation value. In fact, our country's "direct identification method" basically follows this idea.
It should be noted that although the basic methods of identification are the same, the specific implementation rules of each business unit should be differentiated. Only in this way can the final results of the identification be different, in order to reduce the duplication of collections and the omission of valuable documents, and highlight the characteristics Collection. For the comprehensive archives, most of the collections come from the documents formed in important activities of important functional institutions, and the archives kept in the current institutions include not only the documents formed in important functional activities, but also some documents formed in secondary functional activities. . At the same time, in the specific operation process, it is necessary to adopt different strategies according to the national conditions of various countries. If the director of the National Archives of Canada has the right to determine the value of documents, he can directly write to the important agencies of the federal government to announce that the National Archives implements a macro identification strategy. This is difficult to achieve in many other countries.
The key to implementing the basic method of identification and guiding the identification work is that it is not necessary to review all the documents, thus avoiding some scholars pointed out that "in order to select less than 3% of documents for long-term preservation, you must review 100% of documents, which is extremely inefficient." The phenomenon. 1 The provisions of the document storage period table should be specific and operable, and national, local, and various departments should formulate a storage period table applicable to all types of archives at all levels. This is also the premise and basis for the automation of electronic document identification.
If the identification of electronic documents is not much different from the identification of other carrier documents in terms of basic identification methods, then there is a clear difference in the implementation of the methods, mainly reflected in the degree of automation of identification, the identification of received documents, Several aspects such as identification time and identification object.
1. Automatic identification. The computer is the ultimate executor of electronic document authentication and the actual place to save and destroy electronic documents. The computer is first and foremost an automated tool, and archivists have high expectations for the computer's automatic identification of documents. This goal is not fantasy, the key lies in the design of electronic document management system and the establishment of electronic document storage deadlines.
Realize automatic identification, or let the electronic file management system have the function of automatic identification. The method is to include and maintain the electronic file storage period table in the system. The system compares the file with the storage period table to make a judgment. If some new files are not included When the storage period table causes the system to temporarily be unable to judge its storage period, the user shall be promptly prompted to judge; for documents whose storage period has expired, the system automatically prompts the user for the next step of disposal.
In addition, the system should automatically save archived files and delete files that should be destroyed. It is not difficult to see that the electronic document storage period table is an important factor for automatic identification. In addition to specific and operability, the storage period table included in the electronic file management system should also be extensible so as to be updated and supplemented in time . In order to facilitate the comparison between the documents generated in the system and the terms in the storage period table, an expert identification system should be established when necessary.
An expert system is an intelligent system based on a knowledge base. It integrates various knowledge at the time of identification and provides real-time help to online users with the help of computer technology, just like a human expert. The expert system is generally composed of knowledge base, reasoning mechanism, interpretation tool, knowledge acquisition tool and human-machine interface. The knowledge base stores all relevant information, data, rules, cases, and relationships used by the expert system, such as the correspondence between a type of file and its multiple expressions (literature), a variety of relationships between a concept and related concepts, etc. , A knowledge base is very similar to the sum of the knowledge and experience gained by human experts in the field of document identification after many years of work. The inference mechanism searches for information and relationships from the knowledge base and provides answers, predictions, and suggestions in the manner of human experts. The role of the interpretation tool is to allow users to understand how the expert system draws conclusions, that is, to understand the expert's logical reasoning into elements provides a convenient and effective way, it provides users with easy-to-use menus, fill in the appropriate attributes After that, the knowledge acquisition tool stores the information and relationships in the knowledge base. The function of the expert system is to select the corresponding storage period clause or provide suggestions for the file. There is no such expert system yet.
2. Identification of received documents. The development of the network has made the communication between institutions extremely convenient. More and more documents have been transmitted through the network. The typical example is that the upper and lower authorities within the professional system send and receive documents through the local area network, such as many commercial banking systems in China. , Power system, etc. In the identification of paper documents, communications from superior institutions often have permanent or long-term preservation value. In the Internet age, the unit can retrieve the documents issued by the higher authority (that is, the unit's receipt) through the LAN and the document includes background information about when and why the unit was sent.
Therefore, for similar receipts, it is not necessary to save or short-term save after processing. When you need to query and use, you can use the electronic file management system of your unit to find relevant background information left when the file is destroyed; if you need to use the original text, you can Access the database of the higher authority. Of course, using network technology to minimize the phenomenon of repeated storage of electronic files needs to meet certain prerequisites, including a complete network management system, advanced network retrieval technology, complete user permission settings, and mature encryption technology.
3. Identify the object. Regarding this issue, in fact, it has already been mentioned above, that is, the simultaneous identification of the content and technology of electronic files (dual identification) is also known by scholars as identification of usefulness and usability. 1 The former focuses on judging the possible value of the document from the perspective of knowledge utilization. The main criteria are the document formation activities and the links contained in the document. The latter focuses on judging the available status of the file, including the integrity, readability, recording method, carrier status, virus status, and storage fee inspection of the electronic file.
4. Identification time. The identification time of the paper document is generally after the document is formed, and the identification time of the electronic document is advanced to the time when the document is generated or even before it is generated. This is consistent with the goal of the automatic identification of the electronic document management system. Once the document is generated, the system You can use the electronic file storage deadline table (and expert system) to determine the use value of the file and complete real-time identification. In fact, the standard for measuring the value of documents in the system is mainly the functional standard. In this sense, the value of the document is determined by its forming activity, and it is determined before the document is actually produced, so it can be said that the identification work is generated in the document It has been completed before.
Automatically identify the value of electronic files in real time, which is helpful for the long-term management of electronic files. For specific documents, identification is a short-term behavior, and retrieval, utilization, storage, etc. after identification are long-term management behaviors. Due to the characteristics of liquidity, system dependence, etc., electronic documents have many problems related to long-term management. , More urgent issues such as the protection of the integrity and authenticity of electronic files. If real-time identification of documents is carried out and certain documents with preservation value are processed, the probability of sequelae of electronic document management can be effectively reduced. For example, in order to reduce computer storage space and improve work efficiency, it is quite common to establish dynamic links between files. The so-called dynamic connection refers to the changing connection between files, which is generally established through a link operation. The data transferred between files is called an object. Once a link is established between a file and an object, any changes in the object can be automatically reflected in the file. For example, a report on the traffic situation of a city, whose data comes from databases such as urban vehicles and roads, so the information about the report may exist in different systems, machines, and even regions, and the application that generates the report only saves these data. The address and other content information, the corresponding data is still stored in the original database system. The identification of such files is a new issue in the era of electronic files. Once the file is identified as an archive file, the system should store this file. This storage is different from the saved file of the file generation program, but it contains all the information of the file. Content storage, including all data and its address, if necessary, also need to save the database that provides the data source.
â‘ â‘¡ F * Gerald. Ham: "Archive Edge", Liu Yuenan Claudia. Selminny: "Information Technology and User Services", Report of the 14th International Archives Congress.
Terry. Cook, "The Interaction between Archive Theory and Practice since the Publication of the Dutch Manual in 1998", "Report of the Thirteenth International Archives Congress", China Archives Press, 1997 edition.
Richard. Brown: "Choice of Documents and Determination of Value: Macro Appraisal of Documents Stored by the Government within the Scope of Shared Responsibility", "Dynamic Work of Foreign Archives", December 2000.
Harold. Naugler: "Archival Appraisal of Machine Readable Documents :! A copy was published by UNESCO in 1984.
Compiled by Xu Yin: "Identification of Electronic Documents", "Chinese Archives" 2000 Terry. Cook, "The Interaction between Archive Theory and Practice since the Publication of the Dutch Manual in 1998", "Report of the Thirteenth International Archives Congress", China Archives Press, 1997 edition.
Compiled by Liu Yuenan: "Identification of the National Archives of Canada", Lin Da. J Henry: "Report of the Electronic Records Management Committee of the International Archives Council of Schellenberg Theory in the Internet Age:" Review of Electronic Document Management ", http: â‘© Yu Lijuan:" Functional Identification of Electronic Documents "," Beijing Archives "(Beijing) , Zip code: 100872) (Editor Wang Chuanyu)
HDI Printed Circuit Boards - High Density Interconnect PCB Technology
With the development of society, the progress of technology comes from people's constant pursuit of life and their yearning for higher quality of life. Personal consumer electronic products such as notebook computers, personal computers and mobile phones require lighter weight and smaller volume, while smaller volume requires smaller design accuracy and higher density. At the same time, the quality and speed of interconnection technology should be better. This requires designers who make these products to design better components to improve electrical performance, such as circuit boards and so on.
In order to manufacture PCB products of this kind, PCB manufacturers need more advanced manufacturing technology. Of course, from the point of view of product cost, it needs lower cost. This seems contradictory, but HDI PCB can solve this problem very well. HDI PCB has numerous advantages, such as high speed, small size and high frequency.
HDI PCB is the better option for high-layer count and costly laminated boards.
What is a HDI PCB, The definition of HDI PCB
HDI stands for High Density Interconnector, HDI Printed Circuit Board. A circuit board which has a higher wiring density per unit area as opposed to conventional board is called as HDI PCB. HDI PCBs have finer spaces and lines, minor vias and capture pads and higher connection pad density. It is helpful in enhancing electrical performance and reduction in weight and size of the equipment.
High density interconnect (HDI) PCBs represent one of the fastest-growing segments of the Printed Circuit Board market. Because of its higher circuitry density, the HDI PCB design can incorporate finer lines and spaces, smaller vias and capture pads, and higher connection pad densities. A high-density PCB features blind and buried vias and often contains microvias that are .006 in diameter or even less.
Regarding the electrical needs of high-speed signal, the board should have various features i.e. high-frequency transmission capability, impedance control, decreases redundant radiation, etc. The board should be enhanced in the density because of the miniaturization and arrays of the electronic parts. In addition, to the result of the assembling techniques of leadless, fine pitch package and direct chip bonding, the board is even featured with exceptional high-density.
There were a lot of different names for the PCB with such structures. For example, it was called SBU (Sequence Build up the Process) in European and American industry as the program production is in the constructive mode of sequence. It was called MVP (Microvia Process) in Japanese industry because the hole of such products is much smaller than the previous one. It was also called BUM (Build up Multilayer PCB Board ) because the traditional multilayer is known as MLB (Multilayer PCB Board).In order to avoid confusion, IPC Printed Circuit Association proposed to call it HDI (High Density Interconnection Technology) as the common name, but it can not reflect the characteristics of the circuit board. So the majority in the PCB industry define such products as HDI PCB.
Innumerable benefits are associated with HDI PCB, like high speed, small size and high frequency. It is the primary part of portable computers, personal computers, and mobile phones. Currently, HDI PCB is extensively used in other end user products i.e. as MP3 players and game consoles, etc.
HDI PCBs take advantage of the most recent technologies existing to amplify the functionality of circuit boards by means of the similar or little amounts of area. This development in board technology is motivated by the tininess of parts and semiconductor packages that assist superior characteristics in innovative new products like touch screen tabs.
HDI PCBs are described by high-density features comprising of laser micro-vias, high performance thin materials and fine lines. The better density allows extra functions per unit area. These types of multifaceted structures give the required routing resolution for large pin-count chips which are used in mobile devices and other high technology products.
The placement of the parts on the circuit board needs extra precision than conservative board design due to miniature pads and fine pitch of the circuitry on the circuit board. Leadless chips require special soldering methods and additional steps in the assembly and repair process.
The lesser weight and size of the HDI circuitry means the PCBs fit into the little spaces and have a smaller amount of mass than conservative PCB designs. The smaller weight and size even signifies that there is lesser chance of harm from mechanical shocks.
Consumer Driven Technology
The via-in-pad process supports more technology on fewer layers, proving that bigger is not always better. Since the late 1980's we have seen video cameras using cartridges the size of a novel, shrink to fit in the palm of your hand. Mobile computing and working from home pushed technology further to make computers faster and lighter, allowing the consumer to work remotely from anywhere.
HDI Technology is the leading reason for these transformations. Products do more, weigh less and are physically smaller. Specialty equipment, mini-components and thinner materials have allowed for electronics to shrink in size while expanding technology, quality and speed.
HDI PCB Types
According to layer up different, currently DHI board is divided into three basic types:
1) HDI PCB (1+N+1)
Features:
- Suitable for BGA with lower I/O counts
- Fine line, microvia and registration technologies capable of 0.4 mm ball pitch
- Qualified material and surface treatment for Lead-free process
- Excellent mounting stability and reliability
- Copper filled via
Application: Cell phone, UMPC, MP3 Player, PMP, GPS, Memory Card
1+N+1 HDI PCB Structure:
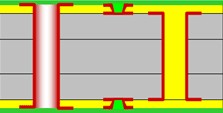
2) HDI PCB (2+N+2)
Features:
- Suitable for BGA with smaller ball pitch and higher I/O counts
- Increase routing density in complicated design
- Thin board capabilities
- Lower Dk / Df material enables better signal transmission performance
- Copper filled via
2+N+2 HDI PCB Structure:
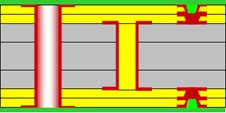
3) ELIC (Every Layer Interconnection)
Features:
- Every layer via structure maximizes design freedom
- Copper filled via provides better reliability
- Superior electrical characteristics
- Cu bump and metal paste technologies for very thin board
Every Layer Interconnection Structure:
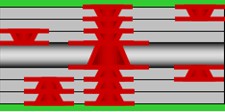
JHY PCB' HDI PCB Capabilities
HDI PCB Manufacturing requires an advanced level of technical expertise and the latest state-of-the-art equipment for exacting precision.
JHY PCB offer solutions for low-volume/high-mix PCB manufacturing on a quickturn basis, as well as production quantities and high-tech capabilities for advanced builds with demanding requirements for aerospace, defense, medical, and commercial applications. Capabilities include:
|
HDI Structures |
Type of Micro vias |
Mass Production |
Small-Middle Batch |
Prototype | Available |
| 1+N+1 | Blind vias | Yes | Yes | Yes | 4 layers+ |
| 2+N+2 |
Blind/Buried staggered vias |
Yes | Yes | Yes | 6 layers+ |
| 2+N+2 |
Blind/Buried stacked vias |
Yes | Yes | Yes | 6 layers+ |
| 3+N+3 |
Blind/Buried staggered vias |
/ | Yes | Yes | 8 layers+ |
| 3+N+3 |
Blind/Buried stacked vias |
/ | / | Yes | 8 layers+ |
Check our HDI PCB capabilities by reviewing the table found below:
| Feature | Capability |
| Quality Grade | Standard IPC 2 |
| Number of Layers | 4 - 24layers |
| Order Quantity | 1pc - 10000+pcs |
| Build Time | 2days - 5weeks |
| Material | FR4 standard Tg 140°C,FR4 High Tg 170°C, FR4 and Rogers combined lamination |
| Board Size | Min 6*6mm | Max 457*610mm |
| Board Thickness | 0.4mm - 3.0mm |
| Copper Weight (Finished) | 0.5oz - 2.0oz |
| Min Tracing/Spacing | 2.5mil/2.5mil |
| Solder Mask Sides | As per the file |
| Solder Mask Color | Green, White, Blue, Black, Red, Yellow |
| Silkscreen Sides | As per the file |
| Silkscreen Color | White, Black, Yellow |
| Surface Finish |
HASL - Hot Air Solder Leveling Lead Free HASL - RoHS ENIG - Electroless Nickle/Immersion Gold - RoHS Immersion Silver - RoHS Immersion Tin - RoHS OSP - Organic Solderability Preservatives - RoHS |
| Min Annular Ring | 4mil, 3mil - laser drill |
| Min Drilling Hole Diameter | 6mil, 4mil - laser drill |
| Max Exponents of Blind/Buried Vias | stacked vias for 3 layers interconnected, staggered vias for 4 layers interconnected |
| Other Techniques |
Flex-rigid combination Via In Pad Buried Capacitor (only for Prototype PCB total area ≤1m²) |
Benefits of HDI PCB Technology with Micro Circuits:
The evolution of high-density PCB technology has given engineers greater design freedom and flexibility than ever before. Designers using HDI high density interconnect methods now can place more components on both sides of the raw PCB if desired. In essence, an HDI PCB gives designers more space to work with, while allowing them to place smaller components even closer together. This means that a high-density interconnect PCB ultimately results in faster signal transmission along with enhanced signal quality.
HDI PCB is widely used to reduce the weight and overall dimensions of products, as well as to enhance the electrical performance of the device. The high-density PCB is regularly found in mobile phones, touch-screen devices, laptop computers, digital cameras and 4G network communications. The HDI PCB is also prominently featured in medical devices, as well as various electronic aircraft parts and components. The possibilities for high-density interconnect PCB technology seem almost limitless.
- Shorter PCB manufacturing lead times and improved device performance for Flip Chip, BGA, MCM, SIP technologies and medical devices.
- Allows utilization of technologies that require ultra thin cores, fine line geometries and alternative via technologies for enhanced thermal transfer in the case of a thermal PCB.
- Allows utilization of the technologies that require 20um circuit geometries, 30um dielectric layers, 50um laser vias and 125um bump pitch processing.
- Allows reducing the [time to market" equation by combining the process capabilities with a strong comprehension of high speed digital and high frequency RF PCB package requirements.
- Increases the area for the PCB designer provider to place circuit components as the components are decreased in size and spaced much closer together. This also improves faster signal transmission and reduced signal loss.
HDI PCB Applications
HDI PCBs are appropriate for a wide range of industries. As mentioned above, you'll find them in all types of digital devices, like smartphones and tablets, where miniaturization is key to the effective application of the product. You can also find high-density interconnect PCBs in automobiles, aircraft and other vehicles that rely on electronics.
One of the most critical areas where the high-density PCB is making huge inroads is in the medical arena. Medical devices frequently need small packages with high transmission rates that only HDI PCBs can supply.
For example, an implant needs to be small enough to fit in the human body, but any electronics involved in that implant absolutely must efficiently allow for high-speed signal transmission. Here, the HDI PCB indeed is a godsend. HDI PCBs can also be useful in other medical equipment, like emergency room monitors, CT scans and much more.
No matter your industry, you're probably already getting some ideas about how high-density interconnect PCBs can make the electronics you produce or use even better - get in touch with us PCBCart to discuss it. We'll let you know if you're on the right track and help you decide exactly how beneficial an HDI PCB can be to your industry. Then, you can determine whether or not to take the next step.
High Density PCBs of Impeccable Quality manufacturer
Over the course of a decade in business, JHY PCB has established a hard-earned reputation for manufacturing PCBs of the highest quality. Our Custom PCB manufacturing capabilities enable you to get the finest quality HDI PCBs at competitive prices without min order quantity requirement. Our team run design for manufacture check on your custom PCB file and consult with you to ensure it is ready for manufacturing and that your boards will meet your performance requirements. We also have an on-site quality control department to verify the finished product meet your high quality standards.
Laser Drill & Laser Direct Imaging: Technology for High Quality HDI PCB Manufacturing.
HDI PCB designs push the limits of technology and JHY PCB is at the forefront of innovation, satisfying the most rigorous requirements.
The demand for HDI PCB manufacturing has been increasing due to the advancements in technology and the many benefits HDI PCBs provide for high-tech applications. Fitting more technology in less space with fewer layers creates limitations for many PCB manufacturers that do not have the specialized equipment and the capacity for advanced features, finer lines, and tighter tolerances.
HDI printed circuit board designs utilize a combination of advanced features like microvias, blind vias, via-in-pad, along with stacked and staggered vias to maximize the the space of the board while increasing its performance and functionality.
JHY PCB achieves high quality and precision with in-house laser drill capabilities that include precise depth control. Laser direct imaging (LDI) capabilities ensure exacting registration and all multilayer inner cores receive a thorough check using Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) units for excellent defect detection of the finest features.
Advanced PCB Materials for HDI PCB Fabrication
JHY PCB offers vast material options for different applications from top manufacturers, such as Isola, Nelco, Arlon, Rogers, and Taconic. Our laminate options offer advanced properties that include:
- High Thermal Reliability
- Ultra-Low Loss
- High Speed Digital
- Halogen-Free
- RoHS Compliant
- Lead-Free High Tg HDI Printed Circuit BoardHDI Printed Circuit BoardHDI Printed Circuit Boards
Additional informations
What is an HDI stackup in Multilayer PCB Design?
HDI PCB
Electronic PCB Board,HDI PCB,HDI Printed Circuit Board,HDI Circuit Board
JingHongYi PCB (HK) Co., Limited , https://www.pcbjhy.com