Discussion on human visual and non-visual biological effects of different light sources
Abstract: This paper starts from the three spectral sensitivity curves of bright vision, dark vision and non-visual, and discusses the effect of light source spectrum on the human body under different visual states. The light environment was evaluated by measuring the spectra of various common light sources, calculating the darkness ratio s/p value and the biological rhythm influence factor acv value. In addition, the distribution of natural light at each hour of the day is selected, the acv value is calculated, and the difference between the artificial light source and the natural light source is compared, thereby obtaining the influence of the color temperature on the s/p value and the acv value, thereby providing an efficient and healthy light source selection. in accordance with.
Keywords: non-visual biological effect s/p value physiological cycle influence factor color temperature
1. Introduction
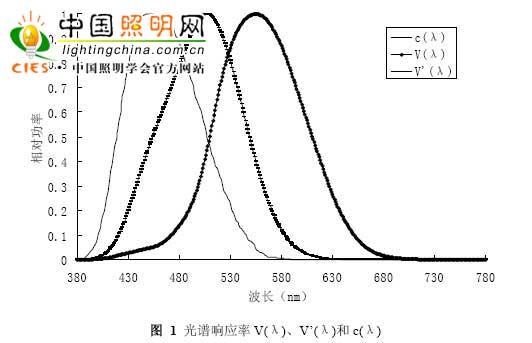
There are three photoreceptor cells in the human eye. Rodial cells and cone cells are most well known. Cone cells play a major role in brightness levels greater than 3 cd/m2, thereby defining clear vision; while rod cells are primarily activated at brightness levels less than 0.001 cd/m2, thereby defining this level of brightness. It belongs to dark vision. The relative sensitivity of the human eye to light of various wavelengths λ, recognized by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) in 1924, is a spectral luminous efficiency function. The visual spectrum spectral efficiency function V(λ) has a maximum value at 555 nm and a dark visual spectrum optical efficiency function V'(λ) with a maximum value at 507 nm. The third photoreceptor cell of the human eye is a cell that acts on the inhibition of melatonin in the human body, and regulates the biological cycle of the human body. Melatonin is an amine hormone secreted by the pineal gland, and its secretion gradually decreases with age. Melatonin is involved in the regulation of seasonal reproduction as a chemical medium of the photoperiod, and is also an important neuromodulator in the retina. According to previous studies, for healthy humans, the wavelength of 446-477 nm is considered to be the most likely range for melatonin secretion [1]. Therefore, a light source with a high color temperature is more effective for melatonin than a low color temperature source. At present, there is no consensus on the spectral function of melatonin inhibition. Therefore, we use the c(λ) curve defined by Gall based on the relevant experimental results [2], and the 2o-view spectrum of the visual curve is corrected by 1978 Judd-Vos. The efficiency function curve, the dark visual curve is the 1951 CIE dark vision spectral luminous efficiency function curve, as shown in Figure 1. The c(λ) curve shifts to a shorter wavelength than the light-dark visual curve, with a peak near 450 nm.